Authentication Handbook
Categories:
Introduction
cc-backend supports the following authentication methods:
- Local login with credentials stored in SQL database
- Login with authentication to a LDAP directory
- Authentication via JSON Web Token (JWT):
- With token provided in HTML request header
- With token provided in cookie
- Login via OpenID Connect (against a KeyCloak instance)
All above methods create a session cookie that is then used for subsequent authentication of requests. Multiple authentication methods can be configured at the same time. If LDAP is enabled it takes precedence over local authentication. The OpenID Connect method against a KeyCloak instance enables many more authentication methods using the ability of KeyCloak to act as an Identity Broker.
The REST API uses stateless authentication via a JWT token, which means that every requests must be authenticated.
General configuration options
All configuration is part of the cc-backend configuration file config.json.
All security sensitive options as passwords and tokens are passed in terms of
environment variables. cc-backend supports to read an .env file upon startup
and set the environment variables contained there.
Duration of session
Per default the maximum duration of a session is 7 days. To change this the
option session-max-age has to be set to a string that can be parsed by the
Golang time.ParseDuration() function.
For most use cases the largest unit h is the only relevant option.
Example:
"session-max-age": "24h",
To enable unlimited session duration set session-max-age either to 0 or empty
string.
LDAP authentication
Configuration
To enable LDAP authentication the following set of options are required as
attributes of the ldap JSON object:
url: URL of the LDAP directory server. This must be a complete URL including the protocol and not only the host name. Example:ldaps://ldsrv.mydomain.com.user_base: Base DN of user tree root. Example:ou=people,ou=users,dc=rz,dc=mydomain,dc=com.search_dn: DN for authenticating an LDAP admin account with general read rights. This is required for the sync on login and the sync options. Example:cn=monitoring,ou=adm,ou=profile,ou=manager,dc=rz,dc=mydomain,dc=comuser_bind: Expression used to authenticate users via LDAP bind. Must containuid={username}. Example:uid={username},ou=people,ou=users,dc=rz,dc=mydomain,dc=com.user_filter: Filter to extract users for syncing. Example:(&(objectclass=posixAccount)).
Optional configuration options are:
username_attr: Attribute with full user name. Defaults togecosif not provided.sync_interval: Interval used for syncing SQL user table with LDAP directory. Parsed using time.ParseDuration. The sync interval is always relative to the timecc-backendwas started. Example:24h.sync_del_old_users: Type boolean. Delete users in SQL database if not in LDAP directory anymore. This of course only applies to users that were added from LDAP.syncUserOnLogin: Type boolean. Add non-existent user to DB at login attempt if user exists in LDAP directory. This option enables that users can login at once after they are added to the LDAP directory.
The LDAP authentication method requires the environment variable
LDAP_ADMIN_PASSWORD for the search_dn account that is used to sync users.
Usage
If LDAP is configured it is the first authentication method that is tried if a
user logs in using the login form. A sync with the LDAP directory can also be
triggered from the command line using the flag -sync-ldap.
OpenID Connect authentication
Configuration
To enable OpenID Connect authentication the following set of options are
required below a top-level oicd key:
provider: The base URL of your OpenID Connect provider. Example:https://auth.example.com/realms/mycloud.
Full example:
"oidc": {
"provider": "https://auth.server.com:8080/realms/nhr-cloud"
},
Furthermore the following environment variables have to be set (in the .env
file):
OID_CLIENT_ID: Set this to the Client ID you configured in Keycloak.OID_CLIENT_SECRET: Set this to the Client ID secret available in you Keycloak Open ID Client configuration.
Required settings in KeyCloak
The OpenID Connect implementation was only tested against the KeyCloak provider.
Steps to setup KeyCloak:
Create a new realm. This will determine the provider URL.
Create a new OpenID Connect client
Set a Client ID, the Client ID secret is automatically generated and available at the
Credentialstab.For Access settings set:
Root URL: This is the base URL of your cc-backend instance.Valid redirect URLs: Set this tooidc-callback. Wildcards did not work for me.Web origins: Set this also to the base URL of your cc-backend instance.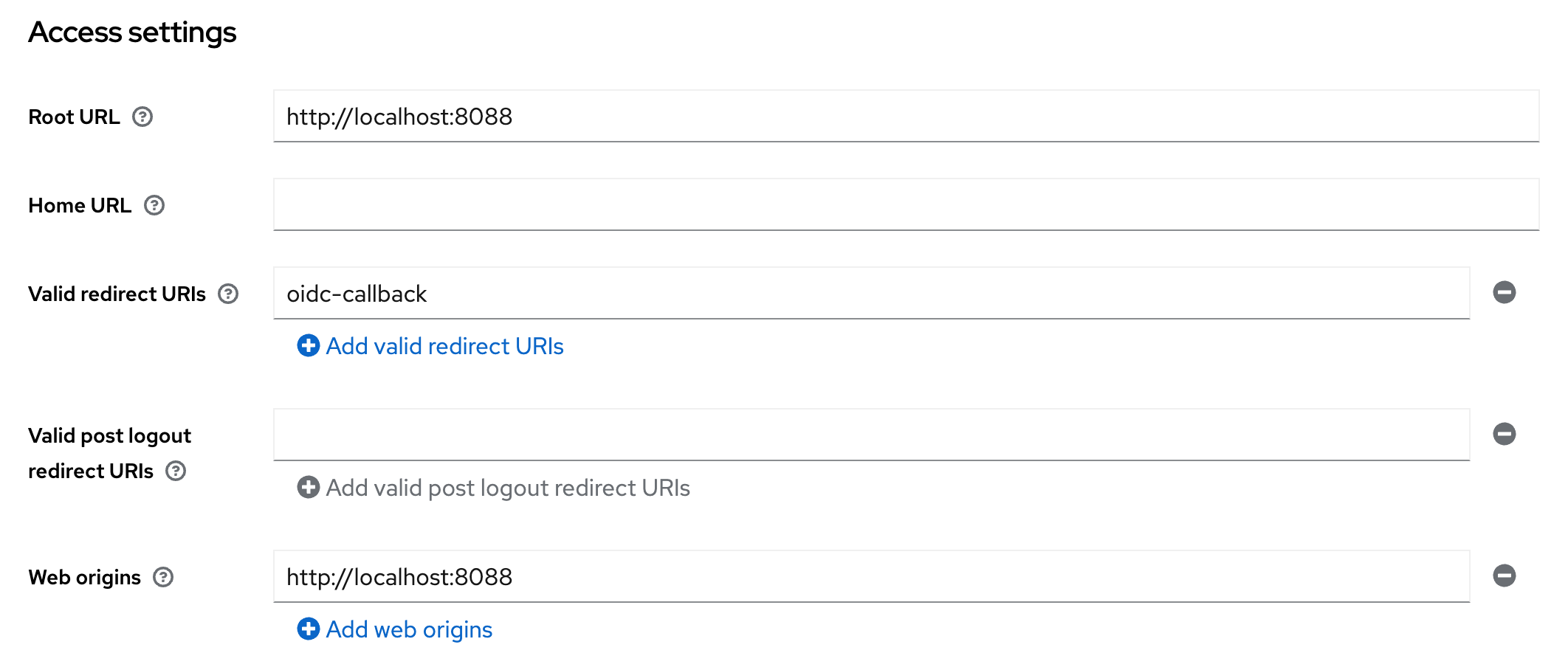
Keycloak client Access settings
Enable PKCE:
- Click on Advanced tab. Further click on Advanced settings on the right side.
- Set the option
Proof Key for Code Exchange Code Challenge MethodtoS256.
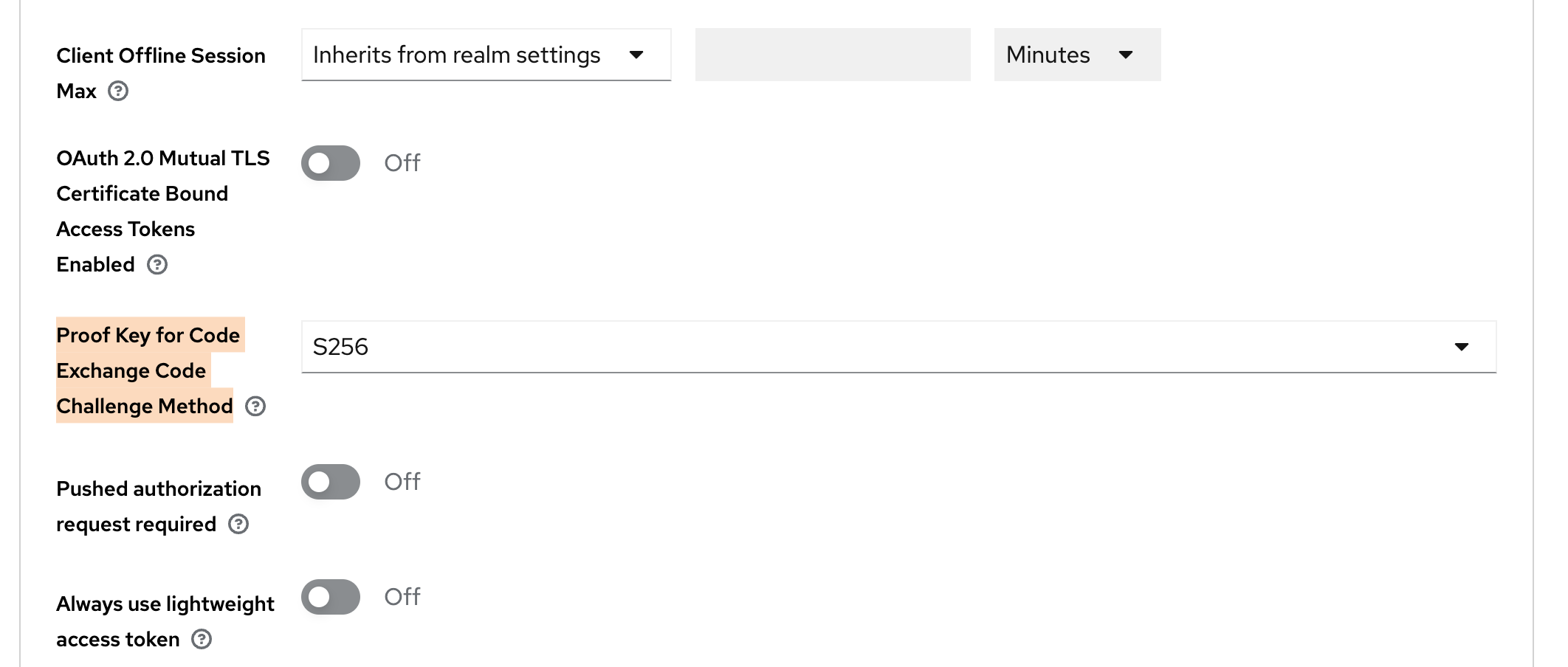
Keycloak advanced client settings for PKCE
Everything else can be left to the default. Do not forget to create users in your realm before testing.
Usage
If the oicd config key is correctly set and the required environment variables
are available, an additional button for OpenID Connect Login is shown below the
login mask. If pressed this button will redirect to the OpenID Connect login.
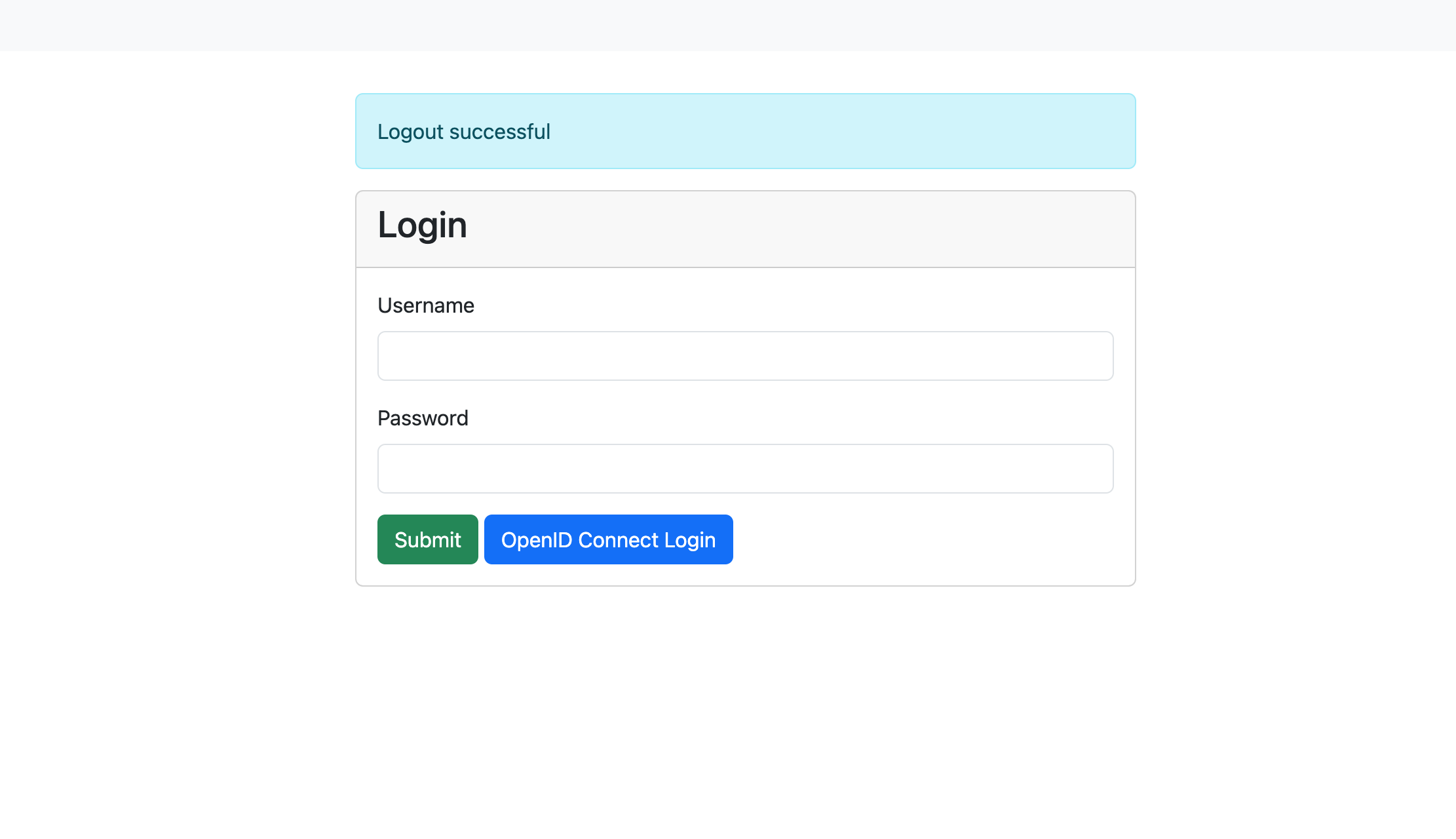
Login mask with OpenID Connect enabled
Local authentication
No configuration is required for local authentication.
Usage
You can add an user on the command line using the flag -add-user:
./cc-backend -add-user <username>:<roles>:<password>
Example:
./cc-backend -add-user fritz:admin,api:myPass
Roles can be admin, support, manager, api, and user.
Users can be deleted using the flag -del-user:
./cc-backend -del-user fritz
Warning
The option-del-user as currently implemented will delete ALL users that
match the username independent of its origin. This means it will also delete
user records that were added from LDAP or JWT tokens.JWT token authentication
JSON web tokens are a standardized method for representing encoded claims securely between two parties. In ClusterCockpit they are used for authorization to use REST APIs as well as a method to delegate authentication to a third party. This section only describes JWT based authentication for initiating a user session.
Two variants exist:
- [1] Session Authenticator: Passes JWT token in the HTTP header Authorization using the Bearer prefix or using the query key login-token.
Example for Authorization header:
Authorization: Bearer S0VLU0UhIExFQ0tFUiEK
Example for query key used as form action in external application:
<form method="post" action="$CCROOT/jwt-login?login-token=S0VLU0UhIExFQ0tFUiEK" target="_blank">
<button type="submit">Access CC</button>
</form>
- [2] Cookie Session Authenticator: Reads the JWT token from a named cookie provided by the request, which is deleted after the session was successfully initiated. This is a more secure alternative to the standard header based solution.
JWT Configuration
- [0] Basic required configuration:
In order to enable JWT based transactions generally, the following has to be true:
- The
jwtsJSON object has to exist withinconfig.json, even if no other attribute is set within.- We recommend to set
max-ageattribute: Specifies for how long a JWT token shall be valid, defined as a string parsable bytime.ParseDuration(). - This will only affect JWTs generated by ClusterCockpit, e.g. for the use with REST-API endpoints.
- We recommend to set
In addition, the the following environment variables are used:
JWT_PRIVATE_KEY: The applications own private key to be used with JWT transactions. Required for cookie based logins and REST-API communication.JWT_PUBLIC: The applications own public key to be used with JWT transactions. Required for cookie based logins and REST-API communication.[1] Configuration for JWT Session Authenticator:
Compatible signing methods are: HS256, HS512
Only a shared (symmetric) key saved as environment variable CROSS_LOGIN_JWT_HS512_KEY is required.
- [2] Configuration for JWT Cookie Session Authenticator:
Tokens are signed with: Ed25519/EdDSA
To enable JWT authentication via cookie the following set of options are required as attributes of the jwts JSON object:
cookieName(String): Specifies which cookie should be checked for a JWT token (if no authorization header is present)trustedIssuer(String): Specifies which issuer should be accepted when validating external JWTs (iss-claim)
In addition, the Cookie Session Authenticator method requires the following environment variable:
CROSS_LOGIN_JWT_PUBLIC_KEY: Primary public key for this method, validates identity of tokens received fromtrustedIssuerand must therefore match accordingly.[3] Optional configuration attributes of the
jwtsJSON object, valid for both [1] and [2], are:validateUser(Bool): Load user by username encoded insub-claim from database, including roles, denying login if not matched in database. Ignores all other claims. By design not combinable with bothsyncUserOnLoginand/orupdateUserOnLoginoptions.syncUserOnLogin(Bool): If user encoded in token does not exist in database, add a new user entry. Does not update user on recurring JWT logins.updateUserOnLogin(Bool): If user encoded in token does exist in database, update the user entry with all encoded information. Does not add users on first-time JWT login.
JWT Usage
- [1] Usage for JWT Session Authenticator:
The endpoint for initiating JWT logins in ClusterCockpit is /jwt-login
For login with JWT Header, the header has to include the Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN information when accessing this endpoint.
For login with JWT request parameter, the external website has to submit an action with the parameter ?login-token=$TOKEN (See example above).
In both cases, the JWT should contain the following parameters:
sub: The subject, in this case this is the username. Will be used for user matching ifvalidateUseris set.exp: Expiration in Unix epoch time. Can be small as the token is only used during login.name: The full name of the person assigned to this account. Will be used to update user table.roles: String array with roles of user.projects: [Optional] String array with projects of user. Relevant if user hasmanager-role.[2] Usage for JWT Cookie Session Authenticator:
The token must be set within a cookie with a name matching the configured cookieName.
The JWT should then contain the following parameters:
sub: The subject, in this case this is the username. Will be used for user matching ifvalidateUseris set.exp: Expiration in Unix epoch time. Can be small as the token is only used during login.name: The full name of the person assigned to this account. Will be used to update user table.roles: String array with roles of user.
Authorization control
cc-backend uses roles to decide if a user is authorized to access certain
information. The roles and their rights are described in more detail here.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.