Overview
What is it?
ClusterCockpit is a framework for job-specific performance and power monitoring on distributed HPC clusters. The focus is put on simple installation and maintenance, high security and intuitive usage. ClusterCockpit provides a modern web interface which provides:
- HPC Users an overview about their running and past batch jobs with access to various metrics including hardware performance counter data. Jobs can be sorted, filtered, and tagged.
- Support staff an easy access to all job data on multiple clusters. Jobs and users can be sorted and filtered using a flexible interface. Job and user data can be aggregated using a customisable statistical analysis. There is a status view providing an overview for all clusters.
- Administrators single file deployment for the ClusterCockpit web backend. A Systemd setup for easy control. RPM and DEB packages for the node agent. For authentication local accounts, LDAP, OpenID Connect, and JWT tokens are supported. There exists an extensive REST API to integrate into an existing monitoring and batch job scheduler infrastructure.
ClusterCockpit is used in production at several HPC computing centers, you can find a list here.
How does it work?
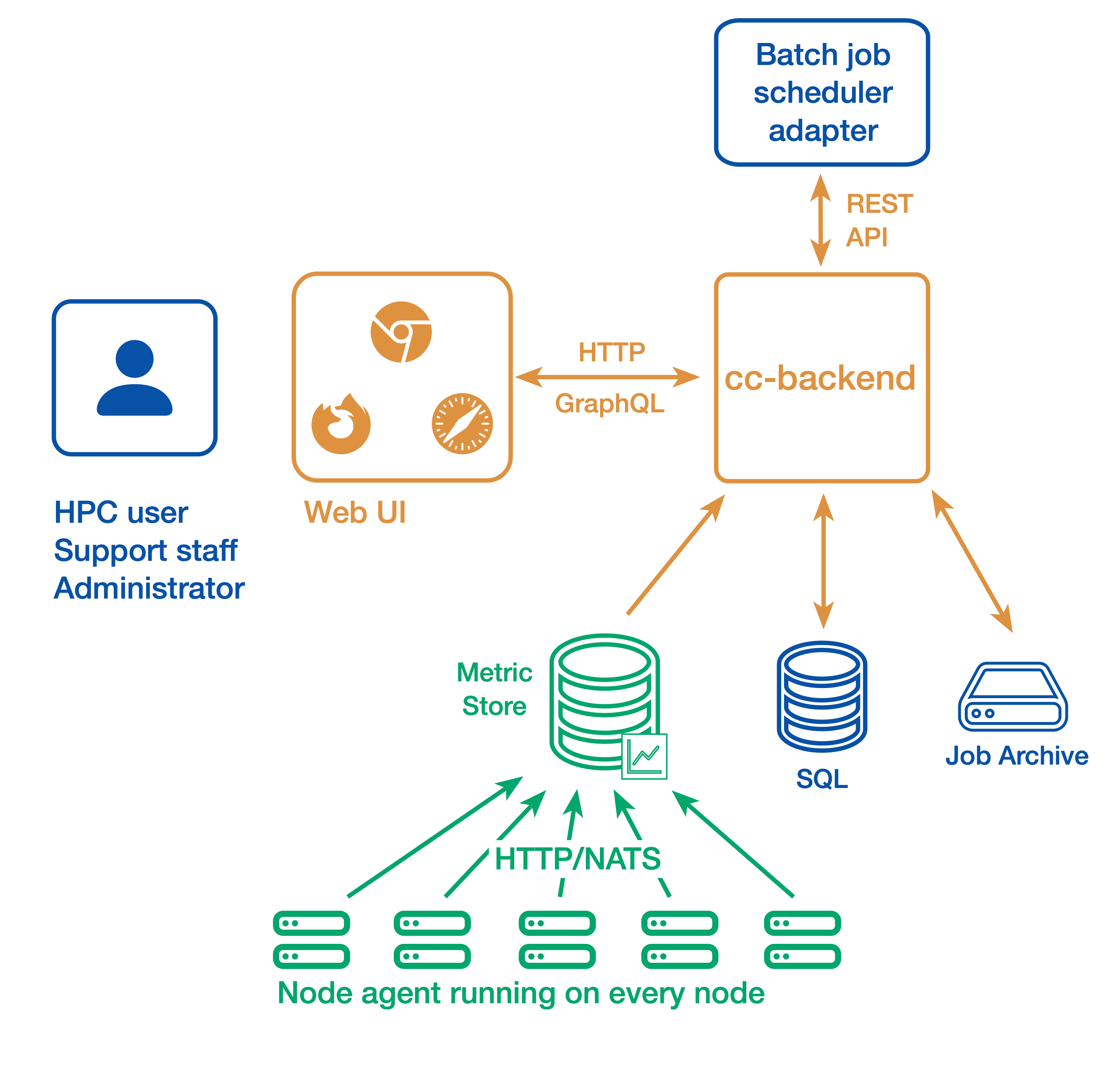
ClusterCockpit consists of
- the web user interface and API backend cc-backend
- the node agent cc-metric-collector
- and the in-memory metric cache cc-metric-store
All components can also be used individually.
Node metrics are collected continuously and sent to the metrics store at fixed intervals. Job details are provided by an external adapter for the batch job scheduler and sent to cc-backend via a REST API. For running jobs, cc-backend queries the metrics store to collect all required time series data. Once a job is finished, it is persisted to a JSON file-based job archive that contains all job metadata and metrics data. Finished jobs are loaded from the job archive. The metrics store uses cyclic buffers and stores data only for a limited period of time.
Where should I go next?
- Getting Started: How to locally setup the ClusterCockpit demo
- Installation manual: How to plan and configure a ClusterCockpit installation
- User guide: A user guide for the ClusterCockpit web interface
Documentation Structure
- Tutorials: Detailed step-by-step lessons how to configure and deploy ClusterCockpit
- How-to Guides: How-to solve concrete problems
- Explanation: Articles about background infos, terms, and concepts in ClusterCockpit
- Reference: In-depth technical documentation
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.